So, you’ve got yourself a budget laptop and you’re wondering if it’s possible to upgrade the RAM sticks? Well, the answer is a resounding yes! Swapping out RAM sticks in a budget laptop is not only possible but can also be a cost-effective way to give your device a performance boost. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of upgrading your laptop’s RAM, ensuring that you can make the most out of your budget-friendly machine. So, let’s get started!
Understanding RAM
What is RAM?
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a crucial component of your computer that plays a significant role in its overall performance. Unlike the long-term storage provided by a hard drive or SSD, RAM provides temporary storage for data that your computer needs to access quickly. It allows your computer to store and access data that is actively being used, such as open applications and files.
Importance of RAM in a computer
RAM is essential for your computer’s performance because it affects how quickly and efficiently your computer can perform tasks. When you open a program or a file, it is loaded into RAM, allowing your computer’s processor to access the data quickly. The more RAM your computer has, the more data it can store and access simultaneously, which leads to faster performance and smoother multitasking.
How RAM affects your computer’s performance
The amount of RAM in your computer directly impacts its performance in various ways. With more RAM, your computer can store and access larger amounts of data, reducing the need to read and write to slower storage devices, such as hard drives. This leads to faster data transfer speeds, less lag when opening applications or files, and improved multitasking capabilities.
Additionally, RAM plays a crucial role in gaming performance. Many modern games require substantial amounts of RAM to run smoothly, as they need to load and store large game files and assets. Insufficient RAM can result in slower load times, choppy gameplay, and overall lower gaming performance.
Types of RAM
DDR1
DDR1, or DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), was the first generation of DDR RAM. It was introduced in 2000 and was used in computers until around 2007. DDR1 RAM has a maximum data transfer rate of 200-400 MHz and is no longer commonly used due to its slower speeds and limited capacity compared to newer generations.
DDR2
DDR2, or DDR2 SDRAM (Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), succeeded DDR1 and was introduced in 2003. DDR2 RAM provides faster data transfer rates, ranging from 400-1066 MHz. Its increased speed and improved efficiency made it popular for several years before being replaced by DDR3.
DDR3
DDR3, or DDR3 SDRAM (Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), was introduced in 2007 and quickly became the standard for most computers. It offers even faster data transfer rates, ranging from 800-2133 MHz. DDR3 RAM is widely used and compatible with a wide range of computer systems due to its affordability and improved performance compared to its predecessors.
DDR4
DDR4, or DDR4 SDRAM (Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), is the current generation of DDR RAM. It was introduced in 2014 and provides even higher data transfer rates than DDR3, ranging from 2133-3200 MHz. DDR4 RAM offers better power efficiency, improved performance, and increased capacity compared to DDR3, making it an excellent choice for gaming and resource-intensive tasks.
DDR5
DDR5, or DDR5 SDRAM (Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), is the upcoming generation of DDR RAM, expected to be released in the near future. DDR5 RAM is anticipated to offer even faster data transfer rates, improved power efficiency, and higher capacities than DDR4.

Limitations of Budget Laptops
Typical hardware specifications
Budget laptops often come with lower-end hardware specifications compared to high-end laptops or desktop computers. They may have slower processors, limited storage space, and, most commonly, smaller amounts of RAM. This limitation can negatively impact a budget laptop’s overall performance, particularly when running resource-intensive applications or multitasking.
Fixed vs. removable components
Another limitation of budget laptops is their limited upgradability. Unlike high-end laptops or desktops that often allow for easy upgrades, budget laptops tend to have fixed components, making it challenging to replace or upgrade certain parts, including RAM. Manufacturers design budget laptops with cost-effectiveness in mind, prioritizing affordability over upgradability.
Manufacturer limitations
Some budget laptop manufacturers intentionally restrict the upgradability of their devices. They may use proprietary designs, such as soldering RAM modules directly to the motherboard, making it impossible or extremely challenging for users to replace or upgrade the RAM themselves. This limitation forces users to purchase higher-priced models or more expensive upgrades directly from the manufacturer.
Feasibility of Swapping RAM Sticks in a Budget Laptop
Physical RAM compatibility
Swapping RAM sticks in a budget laptop is feasible if certain conditions are met. Firstly, the physical form factor of the RAM module must be compatible with the laptop. Most laptops utilize smaller RAM modules, known as SO-DIMMs (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Modules), as opposed to the larger DIMMs (Dual In-Line Memory Modules) used in desktop computers. It is crucial to ensure that the RAM module you wish to install in your budget laptop matches the form factor supported by your laptop’s RAM slots.
Motherboard limitations
Even if the physical form factor is compatible, the motherboard in your budget laptop may have limitations on the maximum amount and type of RAM it can support. You need to verify the maximum supported RAM capacity and the specific RAM types, speeds, and configurations that your laptop’s motherboard can accommodate. This information can usually be found in your laptop’s user manual or by visiting the manufacturer’s website.
Operating system limitations
It’s important to consider any potential limitations imposed by the operating system when swapping RAM sticks in a budget laptop. While most modern operating systems support various RAM configurations, older or more limited versions may have restrictions on the maximum amount of RAM they can utilize. Ensure that your operating system can fully utilize the RAM you plan to install.

How to Determine if Your Laptop Supports RAM Upgrade
Checking laptop’s user manual
To determine if your laptop supports RAM upgrades, the first step is to consult the user manual. The user manual will provide information on whether the RAM can be upgraded, the supported RAM types and capacities, and instructions on how to replace or upgrade the RAM modules. If you don’t have a physical copy of the manual, you can often find the manual on the manufacturer’s website.
Using software tools for hardware analysis
If the user manual does not provide sufficient information or is not readily available, you can use software tools for hardware analysis. There are various free software applications available that can provide detailed information about your laptop’s hardware specifications, including the RAM modules installed, their capacities, and compatibility information. Examples of such software tools include CPU-Z, Speccy, and HWiNFO.
Consulting manufacturer’s website
If you’re unable to find the necessary information from the user manual or through software tools, the next course of action is to visit the manufacturer’s website. Most laptop manufacturers provide support sections on their websites, where you can find detailed specifications for each laptop model, including information on RAM compatibility and possible upgrades. Look for your specific laptop model and check for any official documentation or support articles related to RAM upgrades.
Choosing the Right RAM for Your Laptop
Understanding RAM specifications
When choosing the right RAM for your laptop, it’s essential to understand the various specifications associated with RAM. These specifications include the RAM type (DDR3, DDR4, etc.), capacity (measured in gigabytes), speed (measured in MHz), and latency timings. Matching the RAM specifications to your laptop’s requirements ensures compatibility and optimal performance. Refer to your laptop’s user manual or manufacturer’s website for the specific RAM specifications recommended for your model.
Compatibility issues to look out for
Ensure that the RAM you choose is compatible with your laptop’s motherboard and meets the necessary physical and technical requirements. As mentioned earlier, check the form factor (SO-DIMM or DIMM) and the maximum capacity and type of RAM supported by your laptop. Additionally, consider any potential limitations set by the operating system to ensure full compatibility.
Budget considerations
While it’s important to choose RAM that meets your laptop’s requirements, it’s also essential to consider your budget. RAM prices can vary depending on the type, capacity, and performance. Assess your computing needs and allocate a budget that allows for an upgrade with adequate capacity and performance. Remember to compare prices from different vendors to find the best deal without compromising on quality.

Step by Step Guide on Swapping RAM Sticks
Safety precautions
Before swapping RAM sticks, it’s crucial to follow some safety precautions to prevent damage to your laptop and ensure your personal safety. Turn off your laptop and unplug it from the power source. To discharge any static electricity, touch a grounded object or use an anti-static wristband. Handle the RAM modules with care, avoiding excessive force or bending.
Tools you need
To swap RAM sticks, you will need a few basic tools. These typically include a small Phillips screwdriver to remove any access panels or screws securing the RAM slots and, if necessary, an antistatic strap or mat to prevent static discharge. Additionally, having a clean, static-free workspace and a soft, lint-free cloth can help maintain cleanliness during the installation process.
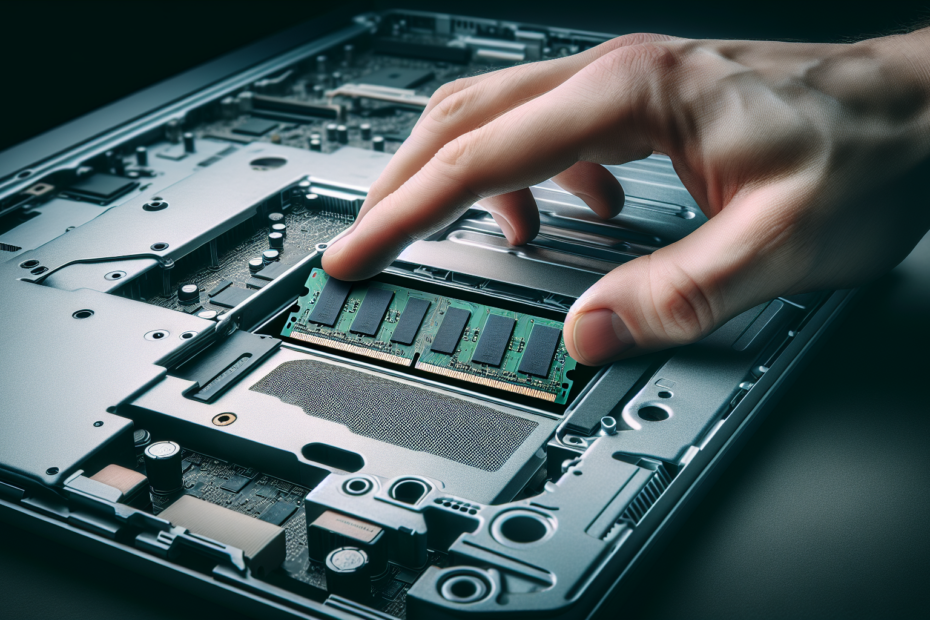
Removing old RAM stick
To remove the old RAM stick, locate the RAM slots on your laptop’s motherboard. Gently spread the retaining clips on either side of the RAM module to release it. Holding the module by its edges, carefully pull it out at a slight angle. If there are multiple RAM modules, remove them one at a time, making sure to keep track of their order and placement.
Installing new RAM stick
Once the old RAM stick is removed, align the notches on the new RAM stick with the ridges in the RAM slot. Insert the module into the slot at a slight angle, ensuring that it is firmly seated. Apply even pressure to both ends of the module until the retaining clips snap into place, securing the RAM stick. Repeat the process if you have multiple RAM modules to install.
Troubleshooting Post Installation Issues
Computer not recognizing new RAM
If your computer does not recognize the newly installed RAM, double-check that the RAM modules are seated correctly and securely in the slots. Ensure that the RAM is compatible with your laptop’s motherboard and meets the required specifications. If the issue persists, try resetting the BIOS settings to their default values or updating the BIOS firmware. If all else fails, consult the manufacturer’s support or seek assistance from a professional.
Performance issues after upgrade
If you experience performance issues after upgrading your RAM, it could be due to incompatible RAM or incorrect module placement. Verify that the RAM you installed matches your laptop’s requirements and is properly seated. In some cases, adjusting the BIOS settings to optimize memory usage may improve performance. If the issues persist, consult the manufacturer’s support or seek professional help.
Reverting to old RAM stick
If you need to revert to your old RAM stick for any reason, power off your laptop and follow the steps outlined in the previous section to remove the new RAM stick. Carefully reinsert the old RAM module into the appropriate slot, ensuring proper alignment and locking it in place with the retaining clips. Power on your laptop to verify that it recognizes the old RAM and functions properly.
Benefits of Upgrading RAM
Improved multitasking performance
Upgrading RAM allows your laptop to handle multiple tasks more efficiently. With more RAM, your laptop can store and access a larger amount of data simultaneously, reducing the need for constant data transfers between RAM and slower storage devices. This leads to improved multitasking performance, allowing you to run more applications and work with larger files without experiencing significant slowdowns.
Faster boot times
Insufficient RAM can cause longer boot times, as the operating system needs to load necessary files and processes into memory. By upgrading your RAM, you can significantly reduce boot times as more data can be stored and accessed quickly. This results in a snappier and more responsive laptop experience from the moment you power it on.
Better gaming experience
One of the most noticeable benefits of upgrading RAM is improved gaming performance. Many modern games require substantial amounts of RAM to run smoothly and load game assets quickly. With more RAM, your laptop can store and access these assets more efficiently, leading to faster load times, reduced in-game lag, and an overall better gaming experience. This is particularly important for resource-intensive games with complex graphics and large worlds.
Alternatives to RAM Upgrade
Clean up your computer
If your budget does not allow for a RAM upgrade, there are alternatives that can help improve your laptop’s performance. Start by decluttering your computer and freeing up valuable storage space by deleting unnecessary files, uninstalling unused applications, and clearing temporary files and caches. Regularly running disk cleanup and disk defragmentation utilities can also help optimize your computer’s performance.
Upgrade to a SSD
Another effective alternative to a RAM upgrade is to replace your laptop’s traditional hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD). SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer speeds and shorter access times compared to traditional hard drives. By upgrading to an SSD, you can experience faster boot times, quicker application loading, and improved overall system responsiveness.
Dealing with software bloat
Software bloat, characterized by excessive and unnecessary background processes and services, can drag down your laptop’s performance. Keep an eye on the applications and services running in the background and disable or remove anything that is not essential. Optimize your startup programs to reduce the number of applications that launch automatically when you boot up your laptop. Regularly updating and maintaining your operating system and installed software can also help keep your laptop running smoothly.
In conclusion, while swapping RAM sticks in a budget laptop is feasible under the right circumstances, it is crucial to consider the physical and technical limitations imposed by the laptop’s design, motherboard compatibility, and operating system requirements. By understanding the specifications, conducting proper research, and following the necessary steps, you can determine if your budget laptop supports RAM upgrades and successfully improve its performance. Whether through a RAM upgrade or alternative methods, such as cleaning up your computer or upgrading to an SSD, investing in improvements will undoubtedly enhance your laptop’s capabilities and provide a more satisfying computing experience.